Unlocking Excel's Full Potential: Mastering Data Visualization in 2025
Excel remains a powerful tool for data visualization. Its accessibility makes it a go-to for many, but creating truly insightful visuals requires more than just clicking the chart button. This article delivers eight data visualization best practices specifically for Excel users. Learn to transform raw data into compelling stories that inform decisions and drive action.
This listicle provides actionable tips to enhance your Excel data visualizations. You’ll discover how to select the right chart type and maximize the impact of your data. We'll explore strategic color use, clear labeling, and the importance of data integrity. These best practices will elevate your reports and dashboards, enabling more effective communication.
We'll cover these key data visualization best practices:
- Choosing the Right Chart Type
- Maintaining a High Data-to-Ink Ratio
- Using Color Strategically and Accessibly
- Starting Bar Charts at Zero
- Crafting Clear Titles, Labels, and Legends
- Optimizing for Audience and Context
- Telling a Story with Data Progression
- Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity
By implementing these data visualization best practices, you'll unlock the full potential of your data and transform your Excel workbooks into powerful communication tools. Supercharge your spreadsheets and enhance your data storytelling.
1. Choose the Right Chart Type for Your Data
Selecting the right chart type is the cornerstone of effective data visualization. It's about matching the visualization to the inherent nature of your data and the story you're trying to convey. This fundamental practice ensures your audience can quickly grasp the information presented. Different chart types excel at highlighting various data relationships, including comparisons, trends, distributions, compositions, and correlations. A poorly chosen chart can obscure insights, while the right one can illuminate them.

Imagine trying to show stock market fluctuations with a pie chart – it simply wouldn't work. This underscores the importance of chart selection in data visualization best practices. Learn more about... choosing the correct chart type and leveraging tools like pivot tables for your data analysis. The right visualization allows your audience to immediately understand complex data points without needing to decipher the underlying numbers. This is crucial for efficient communication and informed decision-making.
Examples of Effective Chart Choices
- Financial Dashboards: Line charts effectively display stock prices over time, showcasing trends and fluctuations.
- Market Research: Pie charts can illustrate market share distribution, providing a clear picture of each competitor's portion of the market. However, keep the number of categories small for optimal readability.
- Scientific Publications: Scatter plots are ideal for correlation analysis, revealing relationships between two variables.
- Business Presentations: Bar charts excel at comparing performance metrics across different categories, offering a quick visual comparison.
Actionable Tips for Choosing the Right Chart
- Comparisons: Use bar charts for comparing discrete categories.
- Trends: Opt for line charts to visualize data trends over a continuous period.
- Correlations: Leverage scatter plots to explore and identify correlations between variables.
- Composition: Utilize pie charts solely for representing parts of a whole, ensuring a limited number of categories for clarity.
- Large Datasets: Consider heat maps to visualize large datasets and uncover hidden patterns.
By carefully considering your data and objective, and applying these tips, you can create compelling visualizations that communicate effectively and drive impactful insights. Choosing the right chart is not merely a stylistic choice, but a crucial step in ensuring the clarity and accuracy of your data story.
2. Maintain High Data-to-Ink Ratio
Maximizing the data-to-ink ratio is a core principle of effective data visualization, championed by Edward Tufte. It emphasizes the importance of minimizing non-data ink, such as excessive gridlines, borders, and decorative elements, while prioritizing the visual representation of the actual data. This results in cleaner, more impactful visualizations that facilitate quicker comprehension. Every element on your chart should contribute directly to understanding the data story. Unnecessary ink only serves to distract and obscure the information you're trying to convey.
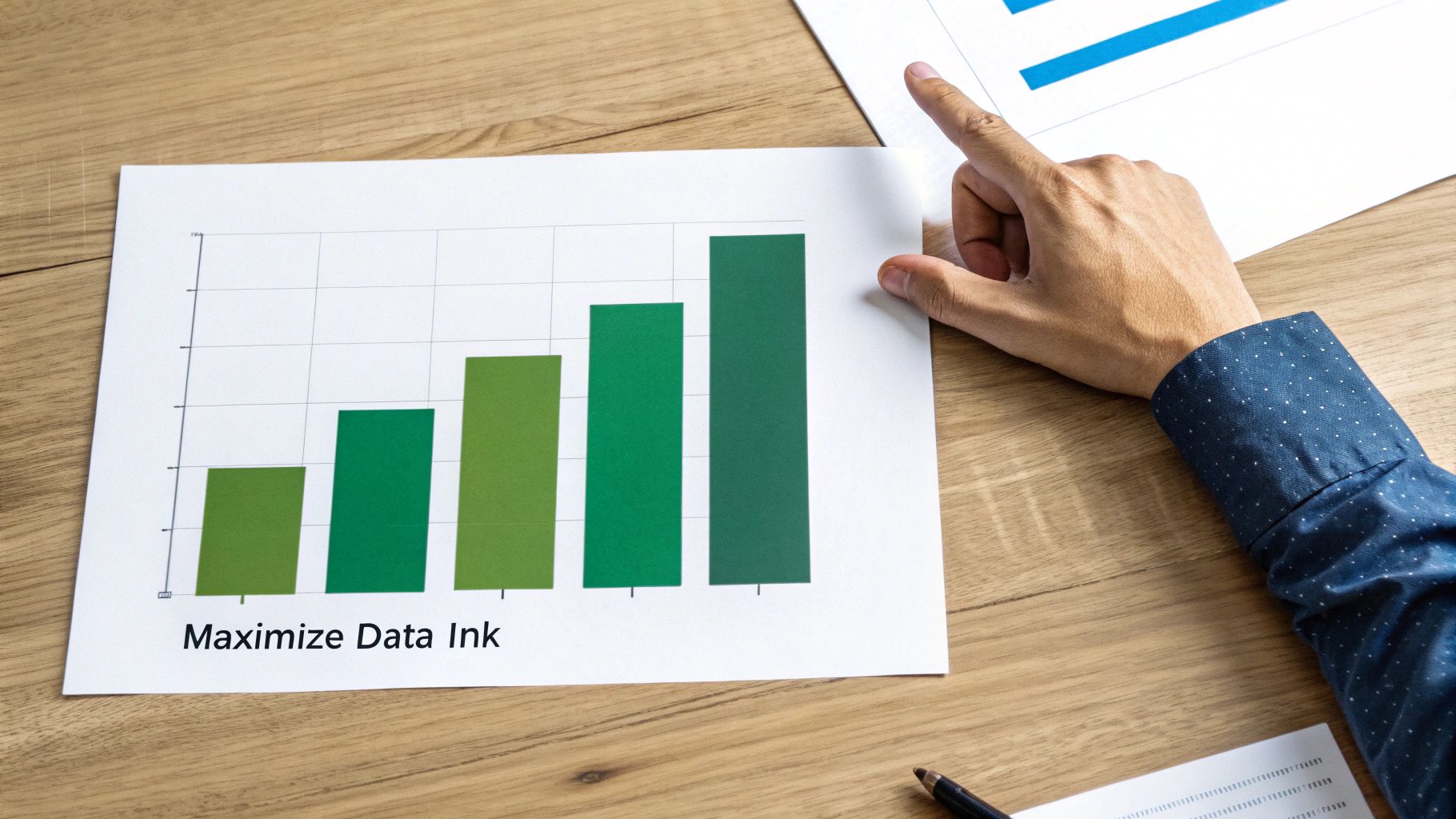

Consider Apple's minimalist design philosophy applied to data presentation; their charts are clean, focused, and prioritize information clarity. Similarly, Google Analytics dashboards effectively employ minimal gridlines and borders, ensuring the data remains the focal point. This principle isn't just about aesthetics; it's about maximizing the effectiveness of your communication. By removing clutter, you allow your audience to focus on the insights, fostering better data-driven decision making.
Examples of Effective Data-Ink Ratio
- Financial Dashboards: Clean line charts showing stock trends with minimal gridlines and a clear focus on price fluctuations.
- Marketing Reports: Bar charts comparing campaign performance with subtle background colors and no chart borders.
- Sales Presentations: Pie charts illustrating market share with muted segment colors and clear data labels, eliminating unnecessary background clutter.
Actionable Tips for Maintaining a High Data-to-Ink Ratio
- Gridlines: Remove unnecessary gridlines and retain only crucial reference lines for context.
- Color Palette: Utilize a subtle color palette for non-data elements, ensuring the data stands out.
- 3D Effects: Avoid using 3D effects and shadows unless they genuinely enhance data interpretation.
- Borders: Reduce border thickness or remove chart borders entirely to minimize visual distractions.
- White Space: Leverage white space effectively to separate chart elements and improve readability.
By applying these data visualization best practices and maximizing your data-to-ink ratio, you can create compelling and easily digestible visualizations that empower your audience to grasp insights efficiently. This is a crucial step in ensuring your data story resonates clearly and drives informed action.
3. Use Color Strategically and Accessibly
Implementing color choices that enhance understanding, guides attention, and remains accessible to all users, including those with color vision deficiencies, is crucial for effective data visualization. Strategic color use involves creating visual hierarchy, encoding data meaningfully, and ensuring sufficient contrast for readability across different viewing conditions and abilities. This best practice elevates data visualization beyond mere aesthetics, transforming it into a powerful communication tool.

Imagine a dashboard where profit is shown in a light green barely distinguishable from the background. This highlights the critical role of strategic and accessible color use. This is particularly important when working with tools like AIForExcel, which can automate much of the visualization process. Ensuring your color choices complement these automated features will enhance the clarity and accessibility of your insights. Thoughtful color application improves comprehension, making your data story accessible to everyone, regardless of their visual capabilities.
Examples of Effective Color Use
- Tableau Dashboards: Tableau's default color palettes are often designed with accessibility in mind, providing a strong starting point for users.
- Scientific Publications: Many scientific journals mandate colorblind-friendly palettes, demonstrating the importance of accessibility in data communication.
- Government Dashboards: Dashboards designed for public consumption often adhere to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards, ensuring broad accessibility.
- Financial Reporting: Progressive financial institutions are moving away from the traditional red/green for profit/loss indicators to more inclusive color schemes.
Actionable Tips for Strategic Color Use
- Accessibility Testing: Use colorblind simulation tools to ensure your visualizations are clear to everyone.
- Accessible Palettes: Utilize tools like ColorBrewer or similar resources to select accessible color palettes.
- Redundant Encoding: Combine color with other visual cues, like patterns or shapes, to reinforce meaning.
- Contrast Ratios: Maintain sufficient contrast ratios (4.5:1 minimum) between foreground and background elements.
- Semantic Colors: Employ semantic colors consistently (e.g., red for negative, blue for neutral) to establish clear visual associations.
By strategically incorporating color into your data visualizations and prioritizing accessibility, you can create impactful and inclusive data stories. This practice is not just about aesthetics; it's about ensuring that your data is understood by the widest possible audience, promoting accurate interpretation and informed decision-making. This is especially important in the context of data visualization best practices, ensuring your work resonates with everyone.
4. Start with Zero on Bar Charts
Starting bar chart axes at zero is a fundamental principle of honest and effective data visualization. It ensures that the visual representation of data accurately reflects the proportional relationships between values. This practice prevents visual distortion that can occur when bar charts use truncated y-axes, which can exaggerate small differences and mislead viewers about the true magnitude of changes or comparisons between categories. A zero-baseline provides a neutral and objective starting point, allowing for a fair assessment of the data.
Imagine two bars on a chart representing sales figures. One bar shows $10 million, and the other shows $11 million. If the y-axis starts at $9 million, the difference appears significant, almost double. However, with a zero baseline, the difference is correctly visualized as a modest 10% increase. This emphasizes the importance of starting at zero for accurate data representation and interpretation.
Examples of Effective Zero-Based Bar Charts
- Sales Performance Dashboards: Accurately depict the relative sales performance across different regions or product lines, avoiding misleading exaggerations.
- Survey Results: Honestly compare response rates across various demographics, providing a clear picture of differences without visual bias.
- Budget Allocation Charts: Present transparent and objective comparisons of budget allocations across departments or projects.
- Academic Research: Represent experimental results with integrity, ensuring the visual display reflects the true magnitude of differences between control and experimental groups.
Actionable Tips for Zero-Based Bar Charts
- Always start at zero: This fundamental rule should be the default for all bar chart visualizations.
- Use gap indicators: If you absolutely must break the axis (e.g., for extremely large values), clearly indicate the break with a visual gap or other indicator.
- Consider alternative chart types: For narrow data ranges, explore alternatives like dot plots or line charts, which might better represent subtle differences.
- Add context or reference lines: Include reference lines or average values to further enhance understanding and provide additional context to the data.
- Include actual values on bars: When precision matters, display the numerical values directly on or next to the bars for clarity.
By adhering to this simple yet powerful practice, you can significantly enhance the clarity, accuracy, and trustworthiness of your bar charts. Starting at zero is not just a visual detail; it’s a crucial step in upholding data visualization best practices and promoting honest data storytelling.
5. Craft Clear and Descriptive Titles, Labels, and Legends
Creating comprehensive and informative text elements is crucial for effective data visualization. Titles, labels, and legends guide viewers, explaining what the data represents and how to interpret the visualization. These elements act as a roadmap, reducing the cognitive load required to understand the visualization and making insights accessible to a broader audience. Good data visualization best practices always prioritize clear communication.
Imagine a chart without a title, axis labels, or a legend. The visual might be appealing, but the meaning is lost without context. This highlights the importance of descriptive text elements in data visualization. Well-crafted titles, labels, and legends transform data into a story, enabling audiences to quickly grasp the main takeaways.
Examples of Effective Text Elements
- New York Times Data Journalism: The New York Times consistently uses explanatory headlines and annotations to provide context and highlight key insights in their data visualizations.
- Corporate Dashboards: Clear KPI definitions accompanying charts in corporate dashboards ensure everyone understands the metrics being tracked and their significance.
- Academic Papers: Comprehensive figure captions in academic publications detail the methodology, data sources, and key findings, allowing for rigorous analysis and reproducibility.
Actionable Tips for Crafting Clear Text Elements
- Titles: Write titles that summarize the key insight revealed by the data, not just the topic. For example, instead of "Sales Data," use a title like "Sales Increased 20% in Q2."
- Labels: Always include units in axis labels (%, $, thousands, etc.) to provide scale and context. Label each axis clearly and concisely.
- Legends: Place legends close to the relevant data whenever possible to avoid confusion. Use distinct colors and clear labels within the legend.
- Annotations: Use annotations to highlight important patterns, outliers, or trends within the data. This draws attention to key details and adds another layer of understanding.
- Data Sources: Include data sources and collection dates to enhance transparency and credibility. This allows viewers to assess the reliability of the data and understand its limitations.
By following these data visualization best practices, you can create visualizations that are not only visually appealing but also easily understood and interpreted. Clear and descriptive titles, labels, and legends ensure that your data story is communicated effectively, leading to better insights and informed decisions. This is not just about aesthetics; it's about making your data accessible and actionable.
6. Optimize for Your Audience and Context
Optimizing for your audience and context is a crucial data visualization best practice. It involves tailoring your visualization design decisions based on your specific audience's expertise, cultural background, viewing environment, and the intended use case. This practice recognizes that the same data might be presented very differently for executives versus technical analysts, or for presentations versus printed reports. Effective data visualization is not one-size-fits-all; it requires careful consideration of who is consuming the information and why.
Imagine presenting a highly technical chart filled with jargon to a non-technical audience. The message would be lost. Similarly, a simplified chart lacking crucial details wouldn't suffice for a specialist needing in-depth analysis. This underscores the importance of audience-centric data visualization in best practice. Tailoring your visualizations ensures that the information resonates with the intended recipients, facilitating understanding and informed decision-making.
Examples of Effective Audience-Specific Visualizations
- Executive Dashboards: High-level Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) presented with clear, concise visuals, focusing on strategic overview.
- Public Health Communications: Simple, easy-to-understand charts for the general public, avoiding technical terminology and complex data representations.
- Technical Documentation: Detailed visualizations with supporting methodology for specialists, enabling deep analysis and scrutiny.
- Mobile-Optimized Visualizations: Charts adapted for smaller screens, ensuring readability and usability for field workers or on-the-go access.
Actionable Tips for Optimizing Your Visualizations
- Know Your Audience: Research your audience's data literacy level and familiarity with specific chart types.
- Context is Key: Consider the decision-making context. What questions are they trying to answer? What actions will they take based on the data?
- Test and Iterate: Test your visualizations with representative users when possible to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement.
- Adapt Detail Level: Adjust the level of detail based on the available viewing time. A presentation requires less detail than a comprehensive report.
- Technical Constraints: Account for technical constraints such as screen size, printing capabilities, and software accessibility.
By carefully considering your audience and context, and applying these tips, you can create visualizations that effectively communicate your data story and drive meaningful insights. Optimizing for your audience is not merely a stylistic choice; it’s a fundamental step in ensuring the clarity, relevance, and impact of your data visualizations. This practice ensures data is presented in a way that truly empowers informed decisions and drives positive outcomes.
7. Tell a Story with Data Progression and Flow
Data visualization is more than just charts and graphs; it's about weaving a narrative that guides your audience through insights. Telling a story with data progression and flow transforms raw numbers into compelling narratives, leading viewers on a journey from initial context to meaningful conclusions. This approach treats data visualization as storytelling, with a clear beginning, middle, and end, ensuring the audience grasps the analysis and its implications. This best practice elevates data visualization from simple reporting to impactful communication.
Think of Hans Rosling's dynamic presentations on global development trends – they captivated audiences by unfolding data narratives over time. Similarly, effective COVID-19 dashboards guided viewers through the progression from cases to outcomes, providing critical context. This storytelling approach applies equally to business quarterly reviews, building from metrics to strategic insights, and investigative journalism, revealing hidden patterns through carefully sequenced data. Learn more about building narratives with data by exploring resources on creating effective KPI dashboards. Learn more about...
Examples of Effective Data Storytelling
- Global Development: Animated visualizations showing changes in life expectancy and income over time.
- Public Health: Dashboards tracking disease outbreaks, visualizing the spread and impact over geographical regions.
- Business Performance: Quarterly reports that progress from overall market trends to specific company performance metrics, culminating in strategic recommendations.
- Investigative Journalism: Data-driven articles that progressively reveal patterns and connections, leading to insightful conclusions.
Actionable Tips for Data Storytelling
- Context is Key: Begin with visualizations that provide context and establish a baseline.
- Visual Consistency: Maintain consistent visual elements (colors, fonts, chart styles) to connect related visualizations.
- Strategic Transitions: Use transitions and animations (where appropriate) to guide the viewer's eye and highlight key changes.
- Clear Conclusions: Conclude with visualizations summarizing key findings and recommending actions.
- The "So What?" Test: Ensure each visualization answers a specific question and contributes to the overall narrative.
By applying these data visualization best practices, you can transform your data from static displays into dynamic stories that resonate with your audience and drive informed decision-making. Data storytelling is essential for effectively communicating complex information and ensuring your insights have a lasting impact.
8. Ensure Accuracy and Data Integrity
Maintaining the highest standards of data accuracy and integrity is paramount in data visualization. This encompasses every stage, from initial data collection and cleaning to the final presentation. Accurate visualizations honestly represent the underlying data, avoiding distortions or misrepresentations that could mislead viewers. This builds trust with your audience and ensures informed decision-making based on reliable insights.
Imagine a medical research visualization misrepresenting clinical trial results due to flawed data – the consequences could be significant. This underscores why data integrity is a non-negotiable aspect of data visualization best practices. Learn more about... effective data cleaning techniques to ensure your foundation is solid. Visualizations should not only be visually appealing but also ethically sound and factually accurate.
Examples of Ensuring Data Integrity
- Medical Research: Visualizations incorporating error bars and confidence intervals transparently communicate the level of uncertainty in the data.
- Financial Reporting: Audited data and clearly stated assumptions provide credibility and context to financial visualizations.
- Survey Results: Displaying sample sizes and margins of error helps viewers understand the representativeness of the data.
- Government Statistics: Providing methodology documentation allows for scrutiny and validation of the data and visualization process.
Actionable Tips for Maintaining Data Accuracy
- Validate Data Sources: Always double-check the reliability and validity of your data sources.
- Indicate Uncertainty: Include visual cues like error bars or confidence intervals when dealing with estimations or projections.
- Document Transformations: Keep a clear record of any data transformations or calculations performed.
- Transparency with Missing Data: Be upfront about any missing or incomplete data and explain how it was handled.
- Regular Audits: Implement regular audit and update processes for ongoing dashboards and reports to ensure accuracy over time.
By adhering to these principles, you create visualizations that are not only visually appealing but also trustworthy and reliable. Data visualization best practices necessitate prioritizing accuracy and integrity – it's not just about aesthetics but about responsible and ethical data representation. This fosters credibility, improves decision-making, and ultimately contributes to a more data-literate world.
Data Visualization Best Practices Comparison
| Item Title | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choose the Right Chart Type for Your Data | Medium – requires knowledge of chart types and data structures | Moderate – requires familiarity with various charts | Clear, accurate data interpretation | Suitable for dashboards, reports, presentations showing diverse relationships | Improves comprehension speed; reduces misinterpretation; enhances professionalism |
| Maintain High Data-to-Ink Ratio | Low to Medium – involves removing non-essential elements | Low – mainly design adjustments in visualization | Cleaner, focused visualizations with better readability | Minimalist dashboards, reports requiring clarity and focus | Reduces clutter; improves readability; reveals data patterns clearly |
| Use Color Strategically and Accessibly | Medium – careful planning and testing for accessibility | Moderate – tools/testing required for colorblind palettes | Enhanced accessibility and visual hierarchy | Visualizations for diverse audiences including color vision deficiencies | Improves data comprehension; guides attention; maintains professional identity |
| Start with Zero on Bar Charts | Low – straightforward but requires discipline | Low – applies mainly to axis settings | Honest data representation; prevents distortion | Bar/column charts illustrating proportional differences | Builds trust; prevents misinterpretation; maintains data integrity |
| Craft Clear and Descriptive Titles, Labels, and Legends | Low to Medium – needs thoughtful text creation | Low – mostly requires time for writing and design space | Self-explanatory, accessible visualizations | Reports, dashboards, academic and journalistic visuals needing clarity | Improves accessibility; reduces cognitive load; enhances credibility |
| Optimize for Your Audience and Context | High – requires audience research and customization | High – may need multiple versions and testing | Increased engagement and comprehension | Audience-specific reports, presentations, and dashboards | Maximizes communication effectiveness; improves decision-making outcomes |
| Tell a Story with Data Progression and Flow | High – requires planning and narrative design | Moderate to High – may involve storytelling and animation tools | Engaging, memorable visualizations | Presentations, storytelling dashboards, investigative reports | Improves retention; guides understanding; makes complex data accessible |
| Ensure Accuracy and Data Integrity | High – demands rigorous validation and transparency | High – effort on data validation, documentation | Trusted, ethical, and reliable visualizations | Scientific, financial, government, and critical decision-making reports | Builds credibility; supports sound decisions; maintains ethical standards |
Elevate Your Excel Expertise: Visualizing Data with Impact
This article has explored eight key data visualization best practices to transform your Excel spreadsheets from static data repositories into dynamic, compelling narratives. We've examined how selecting the right chart type, maintaining a high data-to-ink ratio, and using color strategically can significantly improve the clarity and impact of your visualizations. Furthermore, we've highlighted the importance of starting bar charts at zero, crafting clear titles and labels, and tailoring visualizations to your audience and context.
Key Takeaways for Effective Data Visualization
By consistently applying these principles, you can empower your data to speak volumes, driving informed decisions and actionable insights. Let's recap the most crucial takeaways:
- Accuracy is paramount: Ensure your data is accurate and reliable to maintain credibility and trust.
- Context is king: Understanding your audience and the purpose of your visualization is key to effective communication.
- Simplicity reigns supreme: Avoid clutter and focus on delivering your message clearly and concisely.
From Spreadsheets to Storytelling
Remember, effective data visualization is not just about creating aesthetically pleasing charts. It's about weaving a compelling narrative that resonates with your audience, revealing trends, and highlighting key insights. Implementing these best practices will enable you to unlock the full potential of your data, transforming complex information into easily digestible and actionable knowledge.
Next Steps to Enhance Your Data Visualization Journey
Consider these next steps to further enhance your data visualization journey:
- Practice regularly: The more you experiment with different chart types and visualization techniques, the more proficient you'll become.
- Seek feedback: Share your visualizations with colleagues and solicit constructive criticism to identify areas for improvement.
- Embrace technology: Explore tools designed to enhance Excel's capabilities.
Mastering these data visualization best practices isn't just about creating prettier charts; it's about unlocking the full potential of your data to drive meaningful change and informed decision-making. By effectively communicating your insights, you can influence strategy, improve performance, and achieve your business objectives. As you refine your skills, you'll become increasingly adept at translating raw data into compelling stories that resonate with your audience.
Supercharge your Excel data visualizations with AIForExcel. Seamlessly integrate the power of AI to simplify complex analysis, unlock deeper insights, and create even more impactful visualizations. Visit AIForExcel to learn more and start your free trial today.


